Telehealth in Guatemala: A Case Study in Innovation and Impact
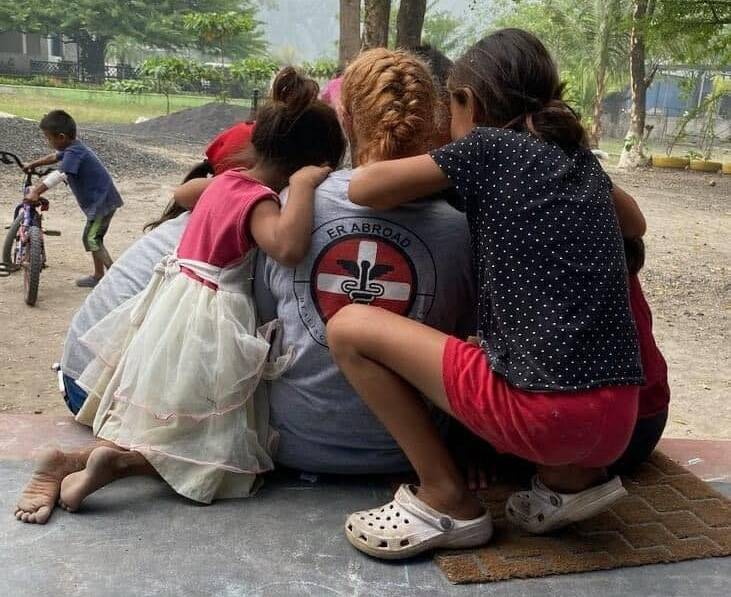
In the rural regions of Guatemala, where poverty and malnutrition rates are high, a telehealth program is making a significant difference. This program, a collaboration between Southern Illinois University Edwardsville, BuildinGuate, and ER Abroad, is not only improving patient outcomes but also providing invaluable experience for nurse practitioner students. A key player in this initiative is BackpackEMR, an electronic medical record (EMR) system that securely stores and tracks patient information.
## Patient Outcomes
According to a research article published in the Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners (2023), while the program is still ongoing, early observations suggest a positive impact on patient outcomes. The telehealth clinics provide continuity of care, particularly for children suffering from malnutrition. Regular follow-ups, made possible by BackpackEMR plus telehealth, are crucial in managing this condition.
However, the program has also highlighted the importance of patient adherence. In some instances, initial weight gain in a child was followed by nonattendance at subsequent clinics and nonadherence to the advice provided by the nurse practitioners. This underscores the need for ongoing patient education and engagement.
## Experience of Nurse Practitioner Students
The telehealth program has proven to be a rich learning environment for nurse practitioner students. They have gained experience in managing diseases not commonly seen in the United States, working with different cultures, and using interpreters. The students have also learned to navigate the challenges of telehealth, such as connectivity issues and data management.
## The Role of BackpackEMR
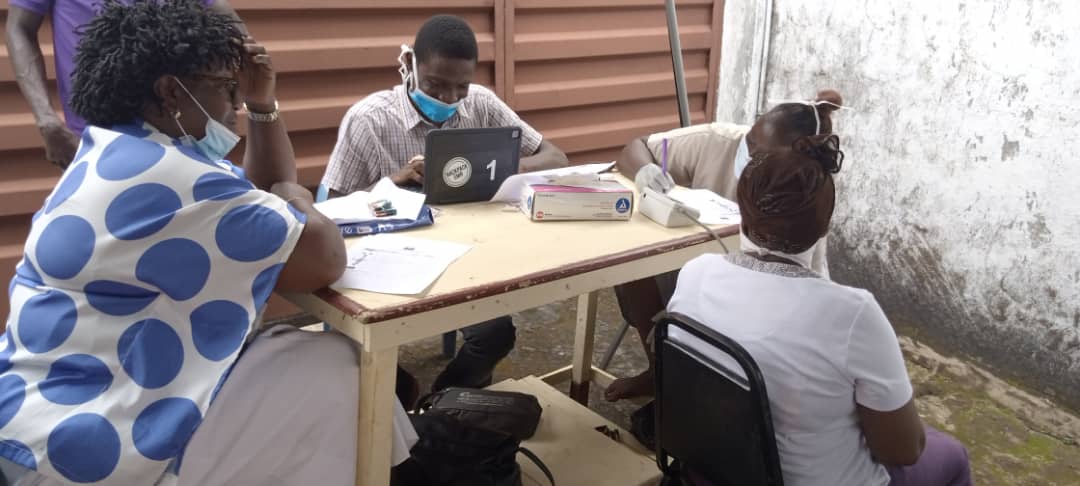
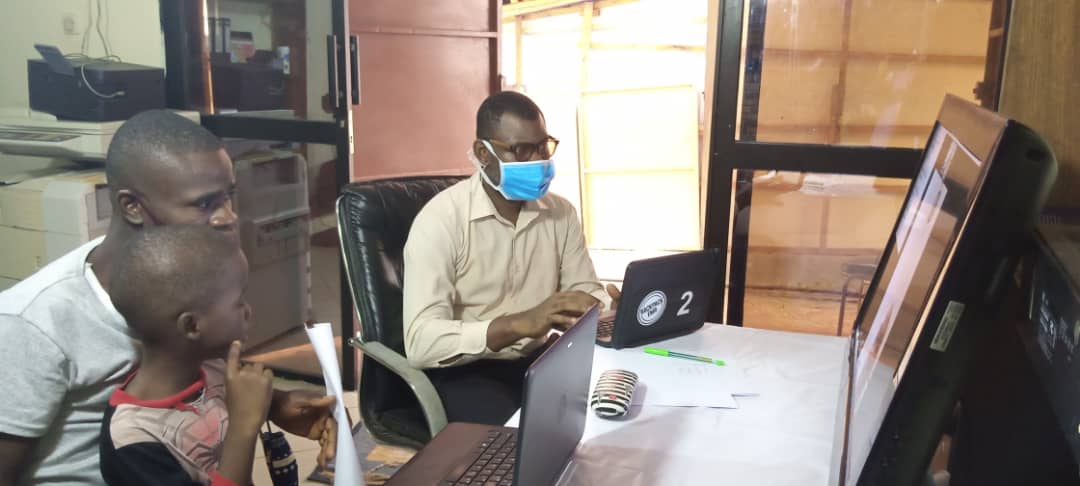
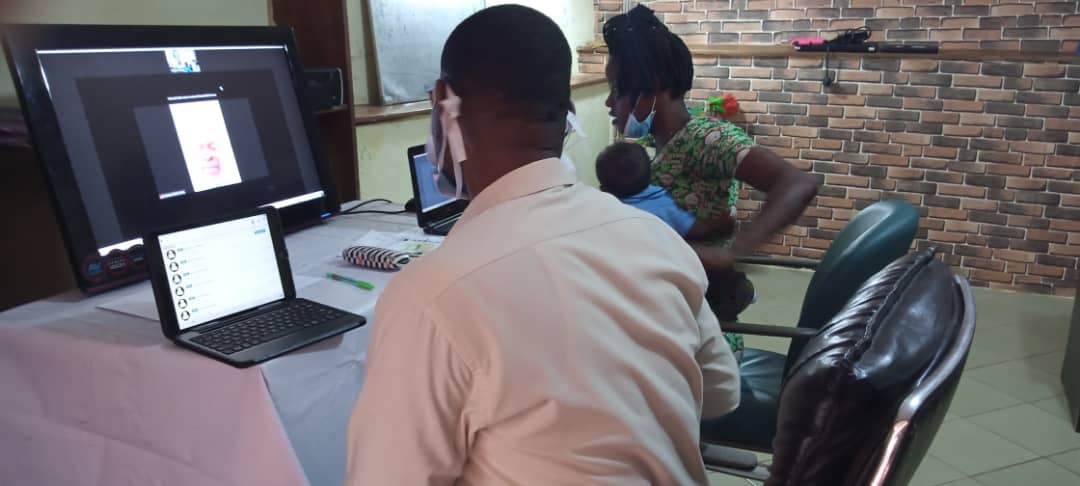
BackpackEMR has been instrumental in the success of the telehealth program. As detailed in the research article, the system securely stores personal health information and tracks patient information from visit to visit. This has been particularly useful in managing chronic conditions like malnutrition, which require regular monitoring and follow-up.
The EMR system also allows for the efficient use of resources. During the telehealth clinics, onsite staff connect to the telehealth system but do not enter data into the EMR. Instead, all medical information is entered by providers in the United States, where internet connections are more reliable.
## Conclusion
The telehealth program in Guatemala, as described in the research article, demonstrates the potential of such initiatives in low-resource settings. It highlights the importance of partnerships, the effective use of technology, and the value of involving nurse practitioner students. The role of BackpackEMR in this program underscores the importance of secure and efficient data management in telehealth. As the program continues, it is anticipated that further patient outcomes will be reported, providing more insights into the effectiveness of this innovative approach to healthcare.